Reading a Tab Delimited File in Matlab
`tab` is used as a separator In the tab-delimited file. This type of text file is created to store various types of text data in a structured format. Unlike types of control be in Linux to parse this type of file. `awk` command is i of the ways to parse the tab-delimited file in different means. The uses of the `awk` control to read the tab-delimited file has shown in this tutorial.
Create a tab-delimited file:
Create a text file namedusers.txtwith the post-obit content to test the commands of this tutorial. This file contains the user'southward proper name, e-mail, username, and password.
users.txt
Name Email Username Password
Md. Robin [email protected] robin89 563425
Nila Hasan [email protected] nila78 245667
Mirza Abbas [email protected] mirza23 534788
Aornob Hasan [e-mail protected] arnob45 778473
Nuhas Ahsan [email protected] nuhas34 563452
Example-i: Print the second column of a tab-delimited file using the -F pick
The post-obit `sed` command will print the 2nd column of a tab-delimited text file. Hither, the '-F' pick is used to define the field separator of the file.
$ cat users.txt
$ awk -F '\t' '{print $2}' users.txt
The post-obit output will appear subsequently running the commands. The 2d cavalcade of the file contains the user's email addresses, which are displaying as output.

Example-2: Print the first column of a tab-delimited file using the FS variable
The following `sed` control volition print the first column of a tab-delimited text file. Here,FS( Field Separator) variable is used to ascertain the field separator of the file.
$ cat users.txt
$ awk '{ impress $ane }' FS='\t' users.txt
The following output will announced after running the commands. The first column of the file contains the user's names, which are displaying as output.

Example-three: Print the third cavalcade of a tab-delimited file with formatting
The following `sed` command will impress the tertiary column of the tab-delimited text file with formatting by using the FSvariable andprintf. Here, theFSvariable is used to define the field separator of the file.
$ cat users.txt
$ awk 'Brainstorm{FS="\t"} {printf "%10s\n", $3}' users.txt
The post-obit output will appear after running the commands. The third cavalcade of the file contains the username that has been printed here.

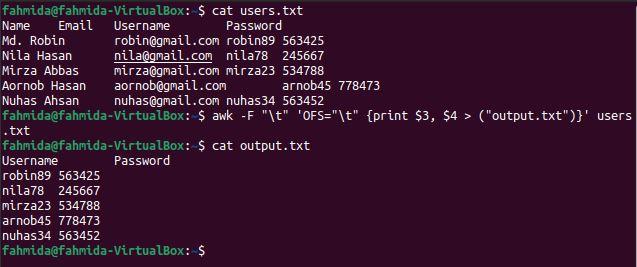
Instance-4: Impress the third and quaternary columns of the tab-delimited file by using OFS
OFS (Output Field Separator) is used to add together a field separator in the output. The post-obit `awk` command volition separate the content of the file based on tab(\t) separator and print the 3rd and 4th columns using the tab(\t) as a separator.
$ true cat users.txt
$ awk -F "\t" 'OFS="\t" {print $three, $four > ("output.txt")}' users.txt
$ true cat output.txt
The following output volition appear after running the above commands. The tertiary and 4th columns contain the username and countersign, which have been printed here.
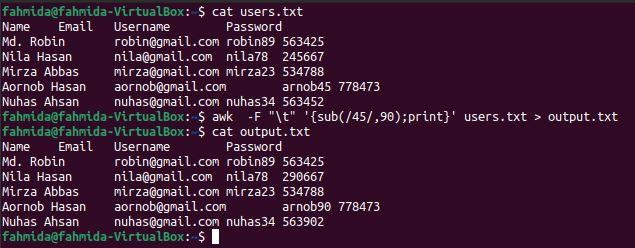
Example-5: Substitute the particular content of the tab-delimited file
sub() function is used in `awk to command for substitution. The following `awk` command will search the number 45 and substitute with the number 90 if the searching number exists in the file. After the exchange, the content of the file will be stored in the output.txt file.
$ cat users.txt
$ awk -F "\t" '{sub(/45/,90);print}' users.txt > output.txt
$ cat output.txt
The following output will announced after running the higher up commands. The output.txt file shows the modified content subsequently applying the commutation. Here, the content of the 5th line has modified, and 'arnob45' is inverse to 'arnob90'.
Example-six: Add string at the beginning of each line of a tab-delimited file
In the following, the `awk` command, the '-F' pick is used to divide the content of the file based on the tab(\t). OFS has used to add a comma(,) every bit a field separator in the output. sub() role is used to add the string '—→' at the commencement of each line of the output.
$ true cat users.txt
$ awk -F "\t" '{{OFS=","};sub(/^/, "---->");print $1,$2,$three}' users.txt
The post-obit output will appear afterward running the above commands. Each field value is separated by comma(,) and a string is added at the outset of each line.

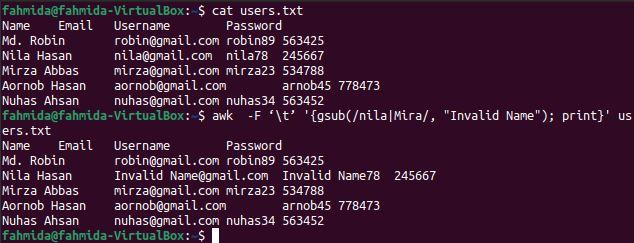
Instance-7: Substitute the value of a tab-delimited file by using the gsub() part
gsub() part is used in the `awk` command for global substitution. All string values of the file volition supplant where the searching pattern matches. The main deviation between the sub() and gsub() functions is that sub() function stops the exchange task after finding the starting time match, and the gsub() function searches the pattern at the end of the file for commutation. The following `awk` command will search the word 'nila' and 'Mira' globally in the file and substitute all occurrences by the text, 'Invalid Name', where the searching word matches.
$ true cat users.txt
$ awk -F '\t' '{gsub(/nila|Mira/, "Invalid Name"); print}' users.txt
The following output will appear afterwards running the in a higher place commands. The word 'nila' exists two times in the tertiary line of the file that has been replaced by the word 'Invalid Proper name' in the output.
Case-8: Print the formatted content from a tab-delimited file
The following `awk` command volition print the offset and the second columns of the file with formatting by using printf. The output will show the user's name past enclosing the email address in brackets.
$ cat users.txt
$ awk -F '\t' '{printf "%s(%south)\northward", $i,$two}' users.txt
The following output volition announced after running the above commands.

Determination
Whatsoever tab-delimited file can exist easily parsed and printed with some other delimiter past using the `awk` command. The ways of parsing tab-delimited files and printing in different formats have shown in this tutorial by using multiple examples. The uses of sub() and gsub() functions in the `awk` command for substituting the content of the tab-delimited file are also explained in this tutorial. I hope this tutorial will assist the readers to parse the tab-delimited file hands after practicing the examples of this tutorial properly.
Source: https://linuxhint.com/parse_tab_delimited_file_using_awk/
Post a Comment for "Reading a Tab Delimited File in Matlab"